Removing Phones from Classrooms Improves Academic Performance
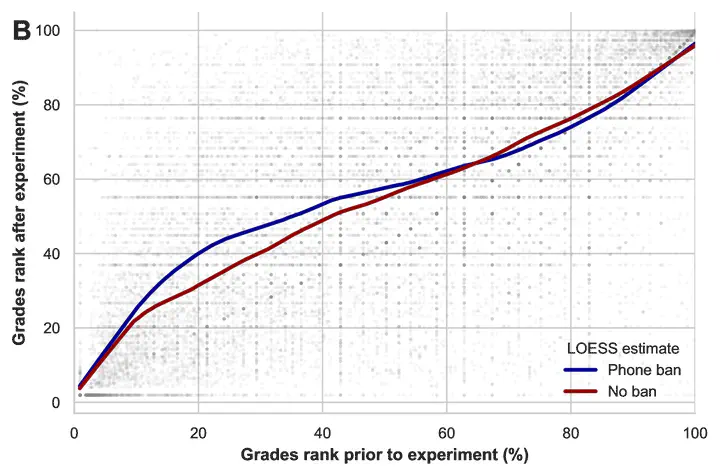
Abstract: Widespread phone bans are being implemented in classrooms worldwide, yet their causal effects on student outcomes remain unclear. In a randomized controlled trial involving nearly 17,000 students, we find that mandatory in-class phone collection led to higher grades — particularly among lower-performing, first-year, and non-STEM students. Importantly, students exposed to the ban were substantially more supportive of phone-use restrictions, perceiving greater benefits from these policies and displaying reduced preferences for unrestricted access. This enhanced student receptivity to restrictive digital policies may create a self-reinforcing cycle, where positive firsthand experiences strengthen support for continued implementation. Despite a mild rise in reported fear of missing out, there were no significant changes in overall student well-being, academic motivation, digital usage, or experiences of online harassment. Random classroom spot checks revealed fewer instances of student chatter and disruptive behaviors, along with reduced phone usage and increased engagement among teachers in phone-ban classrooms, suggesting a classroom environment more conducive to learning. Spot checks also revealed that students appear more distracted, possibly due to withdrawal from habitual phone checking, yet, students did not report being more distracted. These results suggest that in-class phone bans represent a low-cost, effective policy to modestly improve academic outcomes, especially for vulnerable student groups, while enhancing student receptivity to digital policy interventions.